Influence of some chemicals and solvents on the lytic activity and the adsorption of bacteriophages on Pectobacterium carotovoroum Subsp. carotovorum
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14719/pst.2998Keywords:
Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum, Soft rot, Bacteriophages, Pesticides, Fertilizers, SolventsAbstract
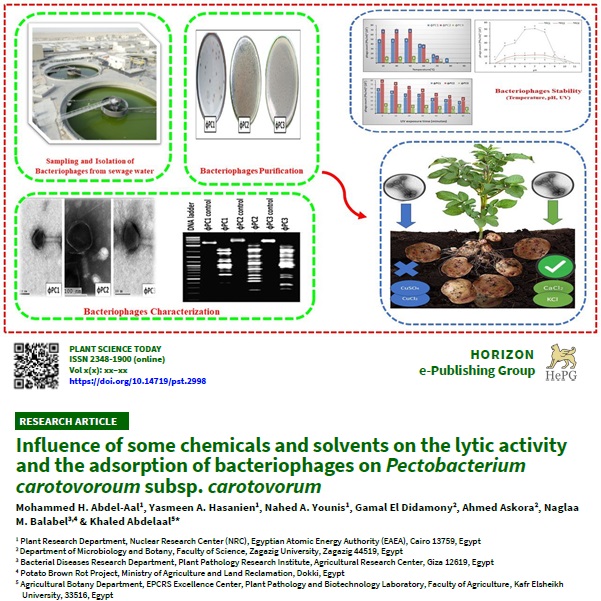
Recently, bacteriophages have been used to control hazardous bacterial soft rot disease on crops. However, agricultural plants are frequently treated with different chemicals (fertilizers, pesticides and solvents), so we assessed the effect of some commonly used chemicals and solvents on the lytic activity of tested bacteriophages and their adsorption potential. This study reports the isolation of three specific phages against the Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum DSM 30170 strain, designated as ?PC1, ?PC2 and ?PC3, then partially characterized using electron microscopy and genome size. The 3 isolated phages belong to the Myoviridae family. The results obtained were based on the plaque-forming unit observed after incubation. By increasing the chemical concentrations (from 0.1 to 0.5 mM), calcium chloride (CaCl2) and potassium chloride (KCl) showed a significant increase in the lytic activity of the phages. Copper sulphate (CuSO4) and copper chloride (CuCl2) showed a substantial decrease in the activity of ?PC3; however, such a decrease was insignificant for ?PC1 and ?PC2. By increasing the solvent concentrations (from 30 % v/v to 70 % v/v), propanol, ethanol and methanol showed a significant decrease in the count of the three isolated phages, ?PC1, ?PC2 and ?PC3, compared to the control. Chloroform was the only solvent that did not reduce the phage titer. Our findings offer significant information for developing a strategy to combat the P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum caused bacterial soft rot disease. avoiding copper compounds and alcoholic solvents such as propanol, ethanol and methanol in plots where phages are applied seems advisable.
Downloads
References
Abd-El-Khair H, Abdel-Gaied TG, Mikhail MS, Abdel-Alim AI, El-Nasr HIS. Biological
control of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum, the causal agent of bacterial
soft rot in vegetables, in vitro and in vivo tests. Bulletin of the National Research Centre.
;45:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-021-00491-4
Abu-Obeid IM. Soft rot disease in Jordan: A review. Advances in Environmental Biology.
;13(6):1-6. http://doi.org/10.22587/aeb.2019.13.6.1
Youdkes D, Helman Y, Burdman S, Matan O, Jurkevitch E. Potential control of potato
soft rot disease by the obligate predators Bdellovibrio and like organisms. Applied and
Environmental Microbiology. 2020;86(6):e02543-02519.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02543-19
Khedr AA. Management of soft rot disease, caused by Erwinia carotovora subsp.
carotovora in potato tubers. African Journal of Biological Sciences. 2019;15(1):211-18. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajbs.2019.72268
Agyemang PA, Kabir MN, Kersey CM, Dumenyo CK. The bacterial soft rot pathogens,
Pectobacterium carotovorum and P. atrosepticum, respond to different classes of
virulence-inducing host chemical signals. Horticulturae. 2020;6(1):13.
https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6010013
Be?o F, Horsáková I, Kmoch M, Petrzik K, Krátká G, Šev?ík R. Bacteriophages as a
strategy to protect potato tubers against Dickeya dianthicola and Pectobacterium
carotovorum soft rot. Microorganisms. 2022;10(12):2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122369
Liang X, Radosevich M, DeBruyn JM, Wilhelm SW, McDearis R, Zhuang J.
Incorporating viruses into soil ecology: A new dimension to understand biogeochemical
cycling. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 2023:1-21.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2023.2223123
Batinovic S, Wassef F, Knowler SA, Rice DT, Stanton CR, Rose J, Tucci J, Nittami T,
Vinh A, Drummond GR. Bacteriophages in natural and artificial environments. Pathogens.
;8(3):100.
Howard-Varona C, Hargreaves KR, Abedon ST, Sullivan MB. Lysogeny in nature:
Mechanisms, impact and ecology of temperate phages. The ISME journal. 2017;11 (7):1511-20. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.16
D’Accolti M, Soffritti I, Mazzacane S, Caselli E. Bacteriophages as a potential 360-
degree pathogen control strategy. Microorganisms. 2021;9(2):261.
https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020261
Czajkowski R, Perombelon MC, van Veen JA, van der Wolf JM. Control of blackleg and
tuber soft rot of potato caused by Pectobacterium and Dickeya species: A review. Plant
Pathology. 2011;60(6):999-1013. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2011.02470.x
Kering KK, Kibii BJ, Wei H. Biocontrol of phytobacteria with bacteriophage cocktails.
Pest Management Science. 2019;75(7):1775-81. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5324
Shang Y, Hasan MK, Ahammed GJ, Li M, Yin H, Zhou J. Applications of nanotechnology in plant growth and crop protection: A review. Molecules. 2019;24(14):2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142558
Itelima J, Bang W, Onyimba I, Sila M, Egbere O. Bio-fertilizers as key player in
enhancing soil fertility and crop productivity: A review. Direct Research Journal of
Agriculture and Food Science. 2018;6(3):73-83. http://hdl.handle.net/123456789/1999
Xi L, Zhang M, Zhang L, Lew TT, Lam YM. Novel materials for urban farming.
Advanced Materials. 2022;34(25):2105009. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202105009
Balogh B, Jones J, Momol M, Olson S. Persistence of bacteriophages as biocontrol
agents in the tomato canopy. In 1st International Symposium on Tomato Diseases. 2004;695:299-302.
AlKhazindar M, Sayed E, Khalil M, Zahran D. Isolation and characterization of two
phages infecting Streptomyces scabies. Research Journal of
Pharmaceutical Biological and Chemical Sciences. 2016;7(2):1351-
Abo-Senna A, El-Fouly M, Hussein H, Swailam H, Abdel-Aal M. Biocontrol of food
borne Salmonella using bacteriophages. Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and
Applications (Online). 2018;51(1):100-09. https://doi.org/10.5771/0010-3497-2018-1-109
Naligama KN, Halmillawewa AP. Pectobacterium carotovorum phage vB_PcaM_P7_Pc
is a new member of the genus Certrevirus. Microbiology Spectrum. 2022;10(6):e03126-32. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.03126-22
Jurczak-Kurek A, G?sior T, Nejman-Fale?czyk B, Bloch S, Dydecka A, Topka G et al. Biodiversity of bacteriophages:
Morphological and biological properties of a large group of phages isolated from urban
sewage. Scientific Reports. 2016;6(1):1-17. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34338
Kalatzis PG, Bastías R, Kokkari C, Katharios P. Isolation and characterization of two
lytic bacteriophages, ?St2 and ?Grn1; phage therapy application for biological control of
Vibrio alginolyticus in aquaculture live feeds. PloS one. 2016;11(3):e0151101. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151101
Phothichaisri W, Ounjai P, Phetruen T, Janvilisri T, Khunrae P, Singhakaew S et al.
Characterization of bacteriophages infecting
clinical isolates of Clostridium difficile. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2018;9:1701.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01701
Akhwale JK, Rohde M, Rohde C, Bunk B, Spröer C, Boga HI, Klenk H-P, Wittmann J.
Isolation, characterization and analysis of bacteriophages from the haloalkaline lake
Elmenteita, Kenya. PLoS One. 2019;14(4):e0215734.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0215734
Othman B, Askora A, Abo-Senna AS. Isolation and characterization of a Siphoviridae
phage infecting Bacillus megaterium from a heavily trafficked holy site in Saudi Arabia.
Folia Microbiologica. 2015;60:289-95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-015-0375-1
Xue Y, Zhai S, Wang Z, Ji Y, Wang G, Wang T et al. The
yersinia phage X1 administered orally efficiently protects a murine chronic enteritis
model against Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2020; 11:351.https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00351
Lee S, Vu N-T, Oh E-J, Rahimi-Midani A, Thi T-N, Song Y-R et al. Biocontrol of soft rot caused by Pectobacterium odoriferum with bacteriophage
phiPccP-1 in Kimchi cabbage. Microorganisms. 2021;9(4):779.
https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040779
El-Afifi S, Hammad A. Biochemical and molecular characteristics of Pc1 virulent phage
isolate infecting Pectobacterium carotovorum. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences:
PJBS. 2020;23(11):1481-86. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2020.1481.1486
Chandrarathna H, Nikapitiya C, Dananjaya S, De Silva B, Heo G-J, De Zoysa M, Lee J.
Isolation and characterization of phage AHP-1 and its combined effect with
chloramphenicol to control Aeromonas hydrophila. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology.
;51:409-16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00178-z
Voronina M, Bugaeva E, Vasiliev D, Kabanova A, Barannik A, Shneider M et al. Characterization of Pectobacterium
carotovorum subsp. carotovorum bacteriophage PP16 prospective for biocontrol of potato
soft rot. Microbiology. 2019;88:451-60. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719040118
Dion MB, Oechslin F, Moineau S. Phage diversity, genomics and phylogeny. Nature
Reviews Microbiology. 2020;18(3):125-38. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0311-5
Kaliniene L, Šimoli?nas E, Truncait? L, Zajan?kauskait? A, Nainys J, Kaupinis A, Valius
M, Meškys R. Molecular analysis of Arthrobacter myovirus vB_ArtM-ArV1: We blame it
on the tail. Journal of Virology. 2017;91(8):e00023-00017.
https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00023-17
Parena AJS, Silva BBI, Mercado RML, Sendon AAA, Signabon FB, Balidion JF, Encabo
JR. Lytic phages display protective effects against soft rot-causing Pectobacterium sp. Biocontrol Science and Technology. 2022;32(11):1326-45.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09583157.2022.2122403
Marei E, El-Afifi SI, Elsharouny T, Hammad AM. Biological control of Pectobacterium
carotovorum via specific lytic bacteriophage. J Basic Appl Sci Res. 2017;7:1-9.
Muturi P, Yu J, Maina AN, Kariuki S, Mwaura FB, Wei H. Bacteriophages isolated in
China for the control of Pectobacterium carotovorum causing potato soft rot in Kenya.
Virologica Sinica. 2019;34:287-94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-019-00091-7
Svircev A, Roach D, Castle A. Framing the future with bacteriophages in agriculture.
Viruses. 2018;10(5):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10050218
Lim J-A, Jee S, Lee DH, Roh E, Jung K, Oh C, Heu S. Biocontrol of Pectobacterium
carotovorum subsp. carotovorum using bacteriophage PP1. Journal of Microbiology and
Biotechnology. 2013;23(8):1147-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1304.04001
Sharma M, Kumar D, Poluri KM. Elucidating the pH-dependent structural transition of
T7 bacteriophage endolysin. Biochemistry. 2016;55(33):4614-25.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00240
Czajkowski R, Ozymko Z, Lojkowska E. Isolation and characterization of novel
soilborne lytic bacteriophages infecting Dickeya spp. biovar 3 (‘D. solani’). Plant
Pathology. 2014;63(4):758-72. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12157
Szermer-Olearnik B, Drab M, M?kosa M, Zembala M, Barbasz J, D?browska K,
Boraty?ski J. Aggregation/dispersion transitions of T4 phage triggered by environmental
ion availability. Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 2017;15(1):1-15.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-017-0266-5
Grass G, Rensing C, Solioz M. Metallic copper as an antimicrobial surface. Applied and
Environmental Microbiology. 2011;77(5):1541-47.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02766-10
Li J, Dennehy JJ. Differential bacteriophage mortality on exposure to copper. Applied and
Environmental Microbiology. 2011;77(19):6878-83.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.05661-11
Buttimer C, Lynch C, Hendrix H, Neve H, Noben J-P, Lavigne R, Coffey A. Isolation and
characterization of Pectobacterium phage vB_PatM_CB7: New insights into the genus
Certrevirus. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(6):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060352
Lukianova AA, Evseev PV, Shneider MM, Dvoryakova EA, Tokmakova AD, Shpirt AM et al.
Pectobacterium versatile
bacteriophage possum: A complex polysaccharide-deacetylating tail fiber as a tool for
host recognition in pectobacterial schitoviridae. International Journal of Molecular
Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911043
Downloads
Published
Versions
- 23-01-2024 (2)
- 16-01-2024 (1)
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Mohammed H Abdel-Aal, Yasmeen A Hasanien, Nahed A Younis, Gamal El Didamony, Ahmed Askora, Naglaa M Balabel, Khaled Abdelaal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright and Licence details of published articles
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Open Access Policy
Plant Science Today is an open access journal. There is no registration required to read any article. All published articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC Attribution 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).









